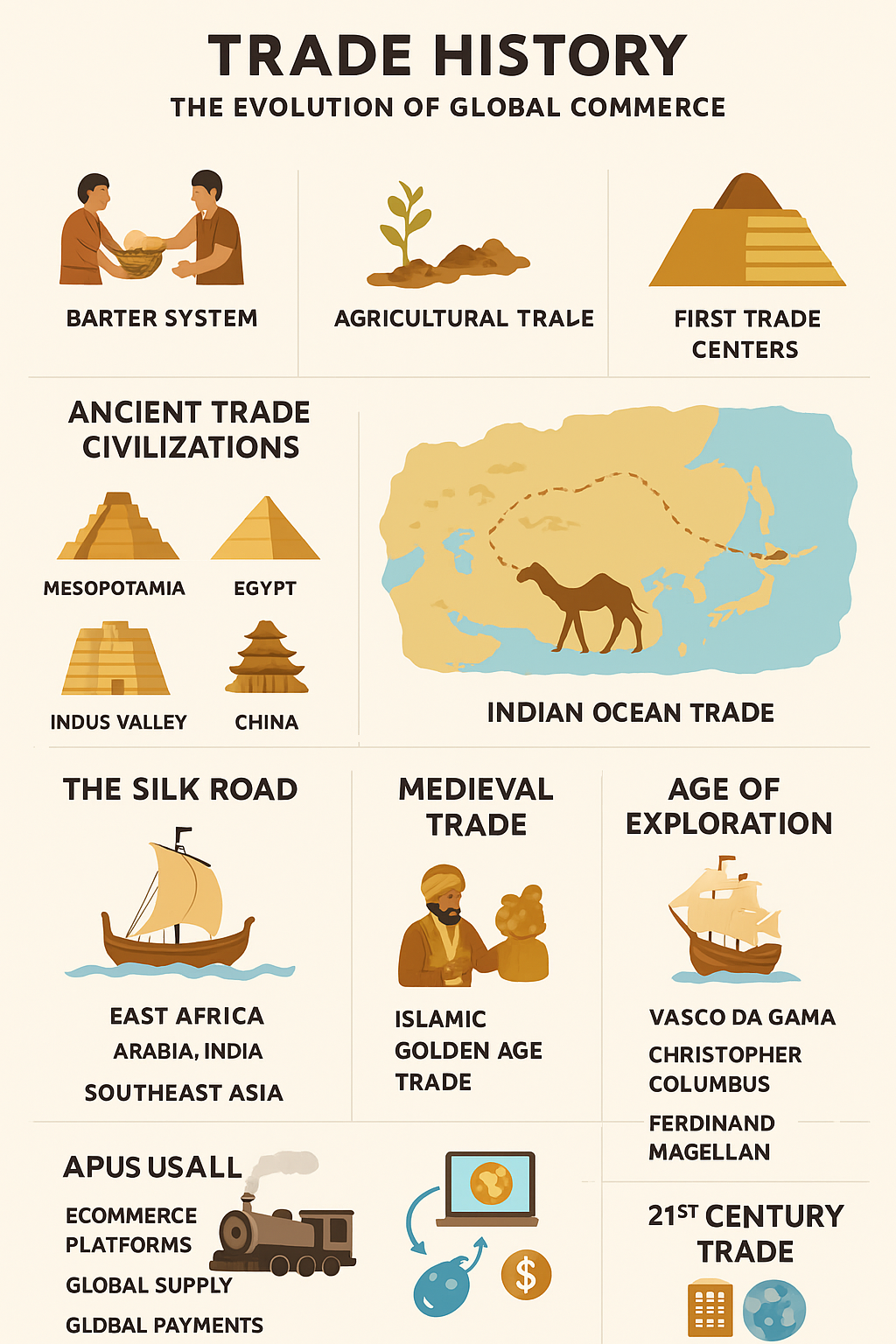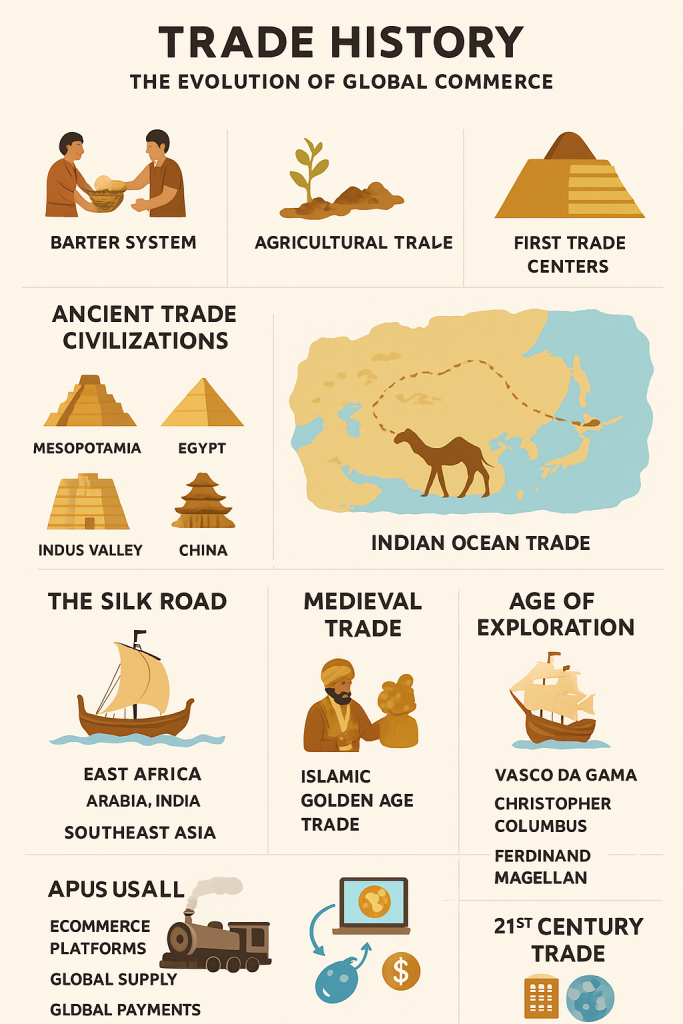
Introduction
Trade history is one of the most important parts of world development. From ancient barter systems to today’s digital global marketplaces, trade has shaped economies, cultures, and political relations. By studying trade history, we understand how societies interacted, how powerful trade routes were built, and how global markets evolved into what we use today. This article explores the complete journey of trade—from ancient times to the modern global economy.
What Is Trade History?
Trade history is the study of how humans exchanged goods, services, and ideas across regions and eras. It includes the growth of market systems, trade routes, merchants, transportation, currencies, and economic policies. Every major civilization participated in trade, and its development helped build cities, expand empires, and connect continents.
Early Trade: The Beginning of Exchange
1. Barter System
The earliest form of trade was barter, where people exchanged goods without money:
- Grain for meat
- Tools for cloth
- Animals for crops
Barter was limited because it required a “double coincidence of wants,” meaning both people had to want what the other offered.
2. Agricultural Trade
When farming began, surplus crops created early markets. People started storing food, which encouraged long-distance exchanges.
3. First Trade Centers
Ancient villages turned into towns because of trade. These centers became busy hubs where merchants met to exchange goods from different regions.
Ancient Trade Civilizations
1. Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is often called the birthplace of trade.
They:
- Invented the earliest writing systems for trade records
- Used clay tablets to track business
- Traded textiles, grain, and metals
2. Egypt
Egypt traded gold, wheat, papyrus, and linen. The Nile River made transportation easy, helping Egypt become a powerful trade empire.
3. Indus Valley Civilization
They traded cotton, beads, spices, and pottery. Their trade network reached:
- Mesopotamia
- Persia
- Central Asia
4. China
China’s most famous contributions to trade were silk, tea, and porcelain. These products later became the foundation of the Silk Road.
The Silk Road: The World’s First Global Trade Network
The Silk Road was one of the most important trade routes in history. It connected:
- China
- India
- Persia
- Arabia
- Europe
Merchants traveled thousands of kilometers carrying:
- Silk
- Spices
- Tea
- Horses
- Precious stones
- Gold and silver
- Ideas and religions
Not only goods but languages, cultures, and technologies spread through this network. The Silk Road helped shape early globalization.
Indian Ocean Trade: Maritime Exchange
When sea travel improved, the Indian Ocean Trade Network became dominant. It connected:
- East Africa
- Arabia
- India
- Southeast Asia
- China
Key goods included:
- Spices
- Ivory
- Gold
- Timber
- Textiles
- Incense
Monsoon winds allowed predictable sailing, making this route safe, fast, and profitable.
Medieval Trade: Rise of Markets and Merchants
During the Middle Ages, trade expanded across Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
1. Islamic Golden Age Trade
Arab merchants controlled routes from Spain to India. They traded:
- Coffee
- Sugar
- Silk
- Precious metals
They introduced banking, checks, and credit systems.
2. Medieval European Trade
Europe saw the rise of:
- Merchant guilds
- Trade fairs
- Market towns
Venice and Genoa became powerful maritime trade cities.
Age of Exploration: The Global Trade Revolution
In the 15th and 16th centuries, European explorers changed world trade forever.
Reasons for Exploration
- Desire for spices
- Search for gold
- New sea routes to Asia
- Expansion of empire
Key Explorers
- Vasco da Gama (India)
- Christopher Columbus (Americas)
- Ferdinand Magellan (World voyage)
Results
- New trade routes
- Discovery of the Americas
- Exchange of crops, animals, and technologies
- Start of colonial trade
However, colonial powers also created exploitation systems, including forced labor and resource extraction.
Industrial Revolution: Modern Trade Begins
The Industrial Revolution transformed global trade:
- Steamships reduced travel time
- Railways connected inland markets
- Factories increased production
- Mass goods became cheaper
- International trade expanded
Countries began exporting manufactured goods and importing raw materials, creating a new global economic structure.
20th Century Trade: Globalization and Modern Markets
The 20th century brought technology, communication, and stable international agreements that made trade faster and easier.
Major Developments
- Introduction of modern banking and finance
- Creation of World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Container ships revolutionizing shipping
- Rise of multinational corporations
- Digital communication and fast payments
Trade barriers were reduced, and global cooperation increased.
21st Century Trade: Digital and Global Economy
Today’s trade is completely different from the past. Technology is the new driver of commerce.
Modern Trade Features
- E-commerce platforms
- Online payments
- Digital products
- Global supply chains
- Instant logistics tracking
- Cryptocurrencies
- AI-driven trade analysis
Companies like Amazon, Alibaba, and eBay created new trade models, connecting buyers and sellers globally in seconds.
Why Trade History Matters Today
Understanding trade history helps us:
- Learn how economies grow
- Understand global connections
- Predict future trade trends
- Improve modern business strategies
- Study cultural and technological exchange
Trade has always been the backbone of human progress.
Conclusion
Trade history shows the journey of human development—from simple barter exchanges to today’s advanced global digital markets. Every stage of history has added new systems, new connections, and new technologies that shaped the world’s economy. Trade built cities, connected continents, and helped different cultures understand each other.
Today’s global trade system is the result of thousands of years of evolution. By studying this history, we understand how deeply trade is linked with human progress—and how it will continue to shape the future.