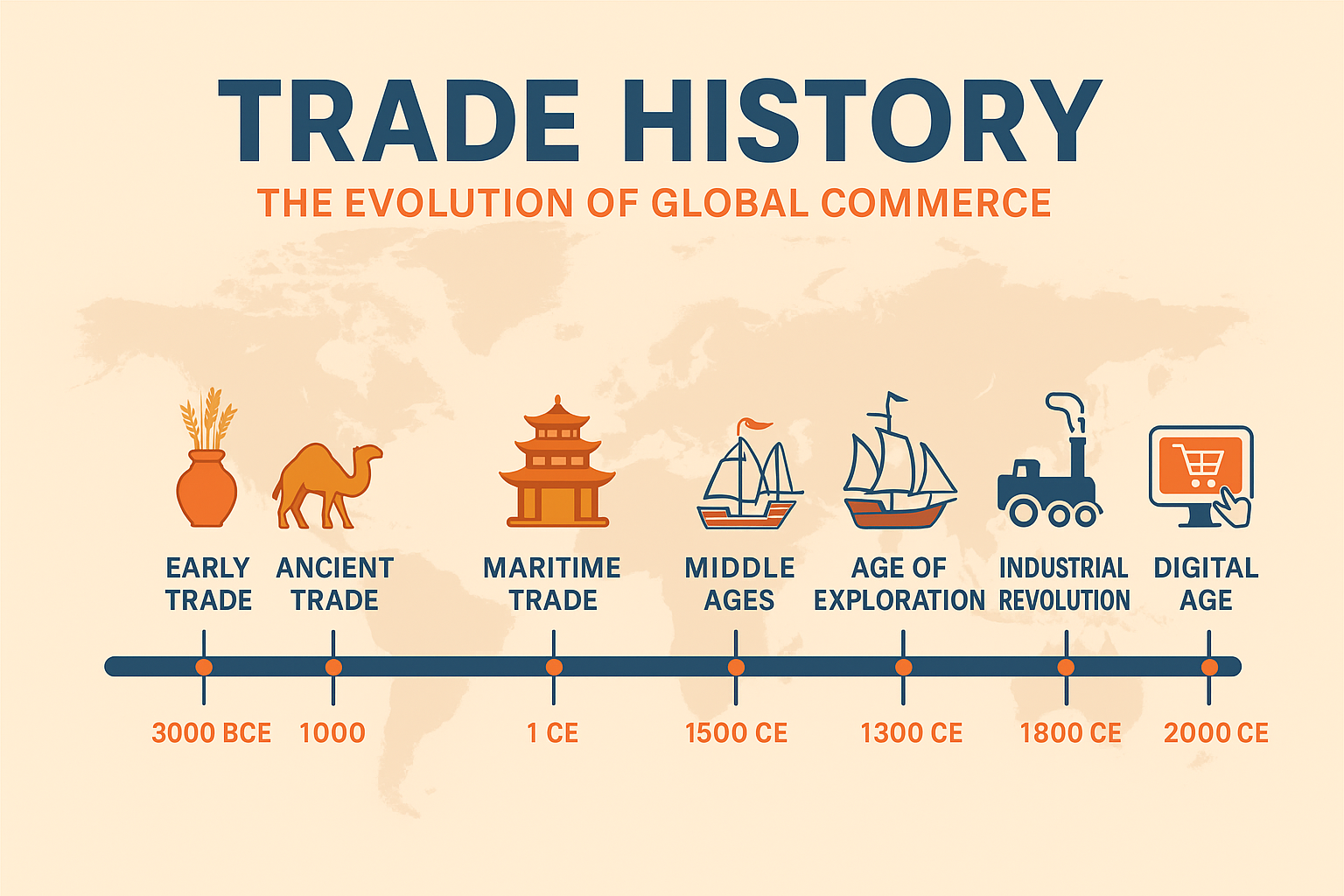
Introduction
Trade history is the story of how humans connected with each other long before modern borders, currencies, or digital markets existed. Trade shaped civilizations, built empires, spread religions, transferred technologies, and created global interdependence.
From bartering food and tools to international shipping and e-commerce, the evolution of trade explains how the world became economically connected.
This article explores the complete journey of trade—from ancient barter systems to today’s global digital economy.
1. Early Trade and the Barter System
The earliest form of trade was barter, a direct exchange of goods.
Common Barter Items
- Grain
- Livestock
- Tools
- Clothing
- Fruits and vegetables
Limitations
- No universal value system
- Needed a “double coincidence of wants”
- Hard to store wealth
These problems led to the invention of currency and structured markets.
2. Agricultural Revolution — Surplus and Early Markets
Once humans learned farming, communities produced surplus food, which encouraged:
- Village marketplaces
- Social classes
- Specialization of labor
- Early long-distance trade
Agriculture laid the foundation for organized trade systems and storage economies.
3. Ancient Civilizations and Trade Networks
Mesopotamia
One of the first regions with commercial trade.
- Developed standardized weights
- Used clay tablets for trade records
- Sold textiles, grain, and pottery
- Traded with Persia, Indus Valley, and Egypt
Ancient Egypt
The Nile River made transportation easier.
- Exported gold, linen, wheat
- Imported spices, incense, timber
- Built international trade with Africa and the Mediterranean
Indus Valley Civilization
Known for maritime trade.
- Standardized weights
- Advanced dockyards
- Exported cotton, beads, and spices
- Traded with Mesopotamia and Central Asia
Ancient China
A major global supplier.
- Silk
- Porcelain
- Tea
- Paper
- Gunpowder
Chinese goods transformed world trade patterns.
4. The Silk Road — The First Global Trade Network
The Silk Road became the biggest historic trade system.
Key Goods
- Silk
- Spices
- Precious stones
- Horses
- Textiles
Cultural Exchange
- Spread of Buddhism, Islam, Christianity
- Introduction of paper and printing
- Artistic and linguistic influences
The Silk Road was not just about trade—it connected entire civilizations.
5. Indian Ocean Trade — The Maritime Superhighway
This network connected Africa, Arabia, India, and China.
Why It Grew
- Predictable monsoon winds
- Safer and faster sea routes
- Large ships that carried bulk goods
Traded Items
- Gold
- Ivory
- Spices
- Fabrics
- Ceramics
The Indian Ocean Region became the center of global commerce for centuries.
6. Medieval Trade — Growth of Markets and Banking
During the Middle Ages, Europe experienced trade revival.
Key Developments
- Merchant guilds
- Trade fairs (France, Italy)
- Rise of Venice and Genoa as maritime powers
- Early banking systems
Merchants became wealthy and influenced politics and culture.
7. Age of Exploration — World Trade Shifts
Between the 15th–17th century, European explorers sailed across oceans.
Reasons
- Search for spices
- New trade routes
- Economic expansion
- Rivalry between European kingdoms
Major Explorers
- Columbus
- Vasco da Gama
- Magellan
Global Impact
- Discovery of the Americas
- Trans-Atlantic trade
- Slave trade
- Spread of crops (potatoes, tomatoes, sugar, coffee)
This era marked the true beginning of global trade.
8. Rise of Colonial Empires
European nations built empires in Asia, Africa, and the Americas.
Colonial Trading Goods
- Spices
- Cotton
- Tobacco
- Sugar
- Tea
- Minerals
Economic Impact
- Colonies supplied raw materials
- Europe produced manufactured goods
- Global trade intensified
Colonialism changed global economic structures permanently.
9. Industrial Revolution — Trade Becomes Global
From the 18th to 19th century, the Industrial Revolution transformed world trade.
New Technologies
- Steam engine
- Spinning jenny
- Railways
- Telegraph
- Electricity
Results
- Mass production
- Cheaper goods
- Faster transportation
- Global supply chains
Factories demanded raw materials, increasing international trade.
10. 20th Century Trade — Wars, Recovery, and Globalization
Impact of World Wars
Wars disrupted trade but led to:
- New technologies
- Formation of international organizations
- Rebuilding of economies
Post-War Global Trade Institutions
- IMF
- World Bank
- GATT (later WTO)
These organizations stabilized world markets.
Containerization
In the 1950s, standardized shipping containers revolutionized logistics.
- Faster shipment
- Lower costs
- Global retail expansion
This created modern supply chain systems.
11. Digital Age — E-Commerce and the New Trade Model
The 21st century introduced digital trade.
Key Elements
- Online marketplaces (Amazon, Alibaba)
- Mobile payments
- Cryptocurrency
- AI-powered forecasting
Digital Goods
- Software
- Streaming content
- Online education
- Digital marketing services
The internet made global trade accessible to everyone.
12. Global Supply Chains
Today’s products are created across many countries.
Example: A smartphone may involve:
- Design in the U.S.
- Chips from Taiwan
- Assembly in China
- Minerals from Africa
- Software updates globally
This interdependence defines modern trade.
Conclusion
Trade history is the story of human connection, innovation, and economic growth.
From ancient barter systems and Silk Road caravans to modern container ships and online marketplaces, trade shaped the world into a global community.
Understanding trade history helps us see:
- How civilizations developed
- How economies became interconnected
- How technology continues to transform commerce
Trade remains the foundation of global progress—and its evolution continues every single day.