Introduction
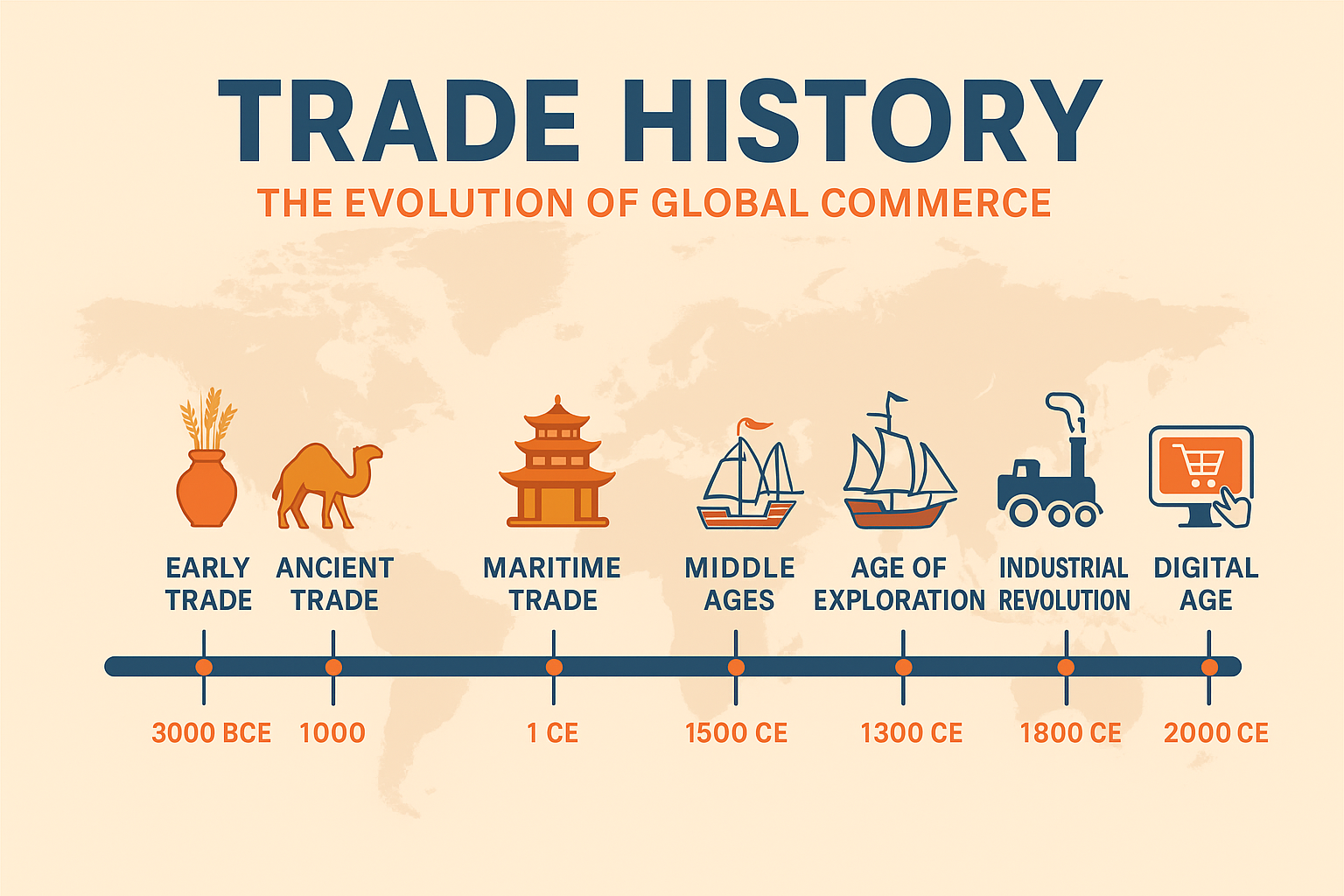
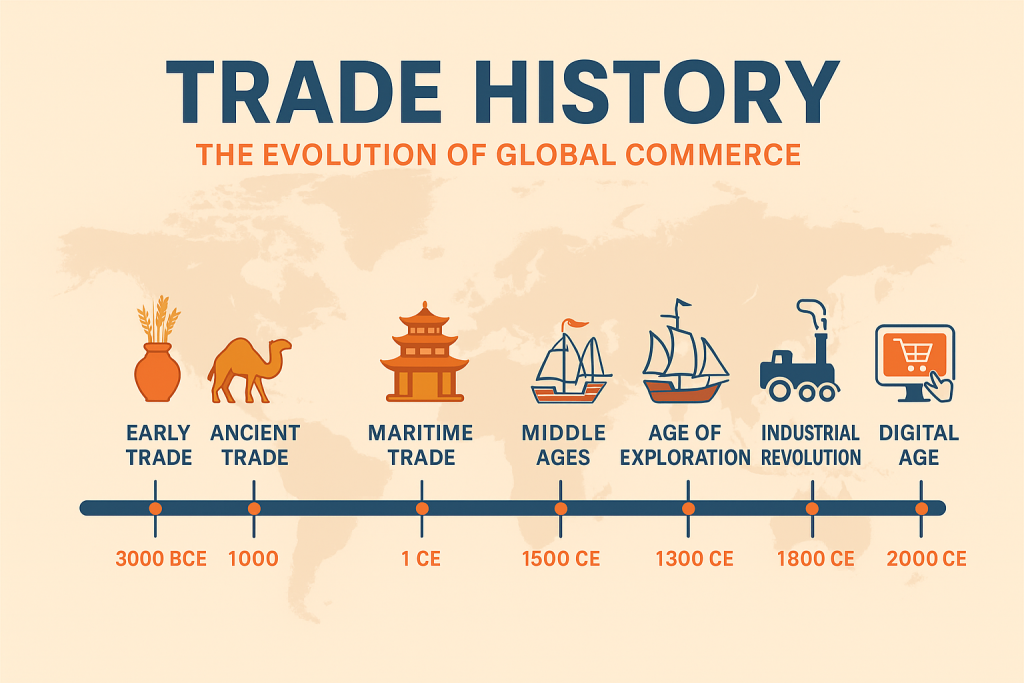
Trade history is one of the most influential forces shaping human civilization. Long before modern economies and digital marketplaces existed, humans exchanged goods, ideas, cultures, and technologies across continents. The story of trade begins with simple barter systems and grows into massive global trade networks that define today’s world economy.
From ancient Silk Road caravans to modern container ships and online marketplaces, trade has continuously transformed societies. This article covers the complete evolution of trade—from ancient times to today’s globalized digital era.
Early Foundations of Trade
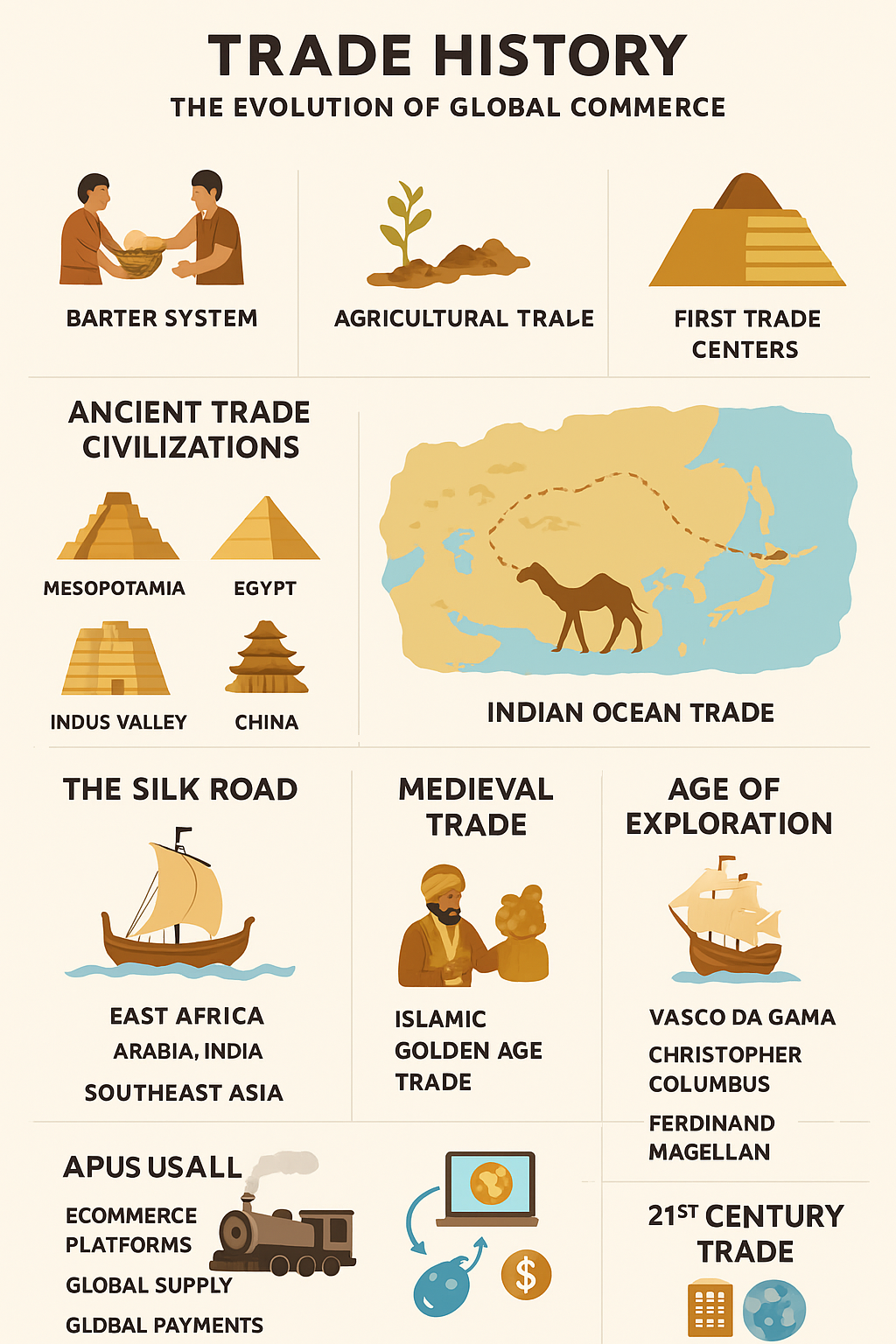
1. Barter System — The Beginning of Exchange
Trade started with the barter system, where people directly exchanged goods without money.
Examples:
- Wheat for livestock
- Tools for clothing
- Spices for metals
Limitations:
- Both parties needed what the other offered
- No standard value system
- Hard to store wealth
This pushed societies to develop more advanced trade systems.
2. Rise of Agriculture and Surplus Production
When humans started farming, they produced surplus food. This allowed communities to exchange extra grain, fruits, and animals for tools and materials.
Surplus encouraged:
- Storage systems
- Early marketplaces
- Specialized labor (farmers, toolmakers, traders)
3. Early Trade Centers and Urban Growth
Trade created early towns and cities. People gathered to buy and sell goods from different regions.
These marketplaces became the world’s first economic zones, leading to the birth of organized trade.
Ancient Trade Civilizations
1. Mesopotamia — The Birth of Commercial Records
Mesopotamia was one of the first regions to develop structured trade.
They introduced:
- Written trade records
- Standard weights and measures
- Trade contracts
- Long-distance routes
Key goods: textiles, grain, metals.
2. Ancient Egypt — River-Based Trade
The Nile River allowed easy transportation. Egyptians traded:
- Gold
- Papyrus
- Linen
- Wheat
They traded with Africa, the Mediterranean, and the Middle East.
3. Indus Valley Civilization — Maritime and Land Trade
The Indus Valley had organized ports and standardized weights.
Trade partners included Mesopotamia, Central Asia, and Persia.
Goods: cotton, beads, pottery, spices.
4. China — Silk, Porcelain, and Innovations
China became a major trade leader due to its unique goods:
- Silk
- Tea
- Porcelain
- Gunpowder
- Paper
China’s products later shaped global commerce.
The Silk Road — The First Great Global Trade Network
1. What Was the Silk Road?
The Silk Road connected Asia, Europe, and parts of Africa.
It was not one road but a network of:
- Land routes
- Caravan paths
- Sea routes
2. Goods Exchanged
- Silk
- Spices
- Tea
- Gold
- Horses
- Precious stones
3. Cultural Exchange
The Silk Road spread:
- Religions (Buddhism, Islam)
- Technologies (paper, printing)
- Languages
- Art and architecture
It was the world’s first major globalization system.
Indian Ocean Trade — A Maritime Powerhouse
1. Largest Sea-Based Trade Network of the Ancient World
This network connected:
- East Africa
- Arabian Peninsula
- India
- Southeast Asia
- China
2. Items Traded
- Spices
- Ivory
- Gold
- Timber
- Textiles
- Incense
3. Monsoon Winds
Predictable winds made travel safer and faster, boosting maritime commerce.
Medieval Trade and New Economic Systems
1. Islamic Golden Age Trade
Arab merchants dominated trade routes from Spain to India.
They introduced:
- Banking systems
- Credit
- Checks
- Advanced navigation tools
2. Medieval Europe
Trade revived with:
- Merchant guilds
- Trade fairs
- Market towns
- Maritime republics (Venice, Genoa)
Europe began building strong commercial economies.
Age of Exploration — The Global Trade Shift
1. Why Exploration Began
Europeans searched for:
- Spices
- Gold
- New sea routes
- Territories
2. Key Explorers
- Vasco da Gama
- Christopher Columbus
- Ferdinand Magellan
3. Impact
- Discovery of the Americas
- Colonization
- Trans-Atlantic trade
- New foods (potato, tomato, maize)
- Global movement of people
The world became interconnected like never before.
Industrial Revolution — Modern Trade Begins
1. Mass Production and Factories
Machines increased goods production.
Results:
- Cheaper products
- Larger markets
- Urban growth
2. Transportation Revolution
- Steamships
- Railways
- Improved roads
- Canals
These innovations created faster, cheaper trade networks.
3. New Global Economic Structure
Countries became interdependent:
- Colonies supplied raw materials
- Europe produced manufactured goods
- Global trade flourished
20th Century Trade — The Era of Globalization
1. World Wars and Trade Disruption
Both world wars damaged global trade but also introduced:
- New industries
- New technologies
- New global alliances
2. Post-War Trade Agreements
Institutions like:
- IMF
- World Bank
- GATT (later WTO)
were created to stabilize global commerce.
3. Rise of Multinational Corporations
Companies expanded worldwide:
- Oil
- Automobiles
- Electronics
- Food chains
4. Container Shipping Revolution
Standardized shipping containers transformed global supply chains.
21st Century Trade — Digital and Hyperconnected
1. E-Commerce
Platforms like:
- Amazon
- Alibaba
- eBay
changed how people buy and sell goods globally.
2. Digital Payments
- Online banking
- Mobile wallets
- Blockchain
- Cryptocurrencies
Payments became instant and borderless.
3. Global Supply Chains
Items like phones and cars involve:
- Multiple countries for parts
- Global factories
- Worldwide logistics
4. AI and Automation
Artificial Intelligence now manages:
- Shipping
- Pricing
- Inventory
- Forecasting
This marks the future of trade.
Conclusion
Trade history is the story of human progress. From simple barter systems to advanced digital markets, trade has connected civilizations, shaped cultures, and built global economies. Ancient routes like the Silk Road evolved into modern global supply chains. Today, digital trade and AI continue to push the world into a new era of economic transformation.
Trade remains the backbone of global development—and its history shows how far humanity has come.