Introduction
Modern History marks one of the most dramatic and influential eras in human civilization. Beginning around the late 15th century and continuing to the present day, this period witnessed sweeping global changes — from the Age of Exploration and the Scientific Revolution to industrialization, world wars, and the digital age. These events did not just shape governments and economies; they changed culture, society, technology, and the way people interact in a globalized world. This article explores the key phases, major turning points, and long-term impacts of Modern History using clear explanations and highly searched keywords to help readers understand how the modern world was built.
What Is Modern History?
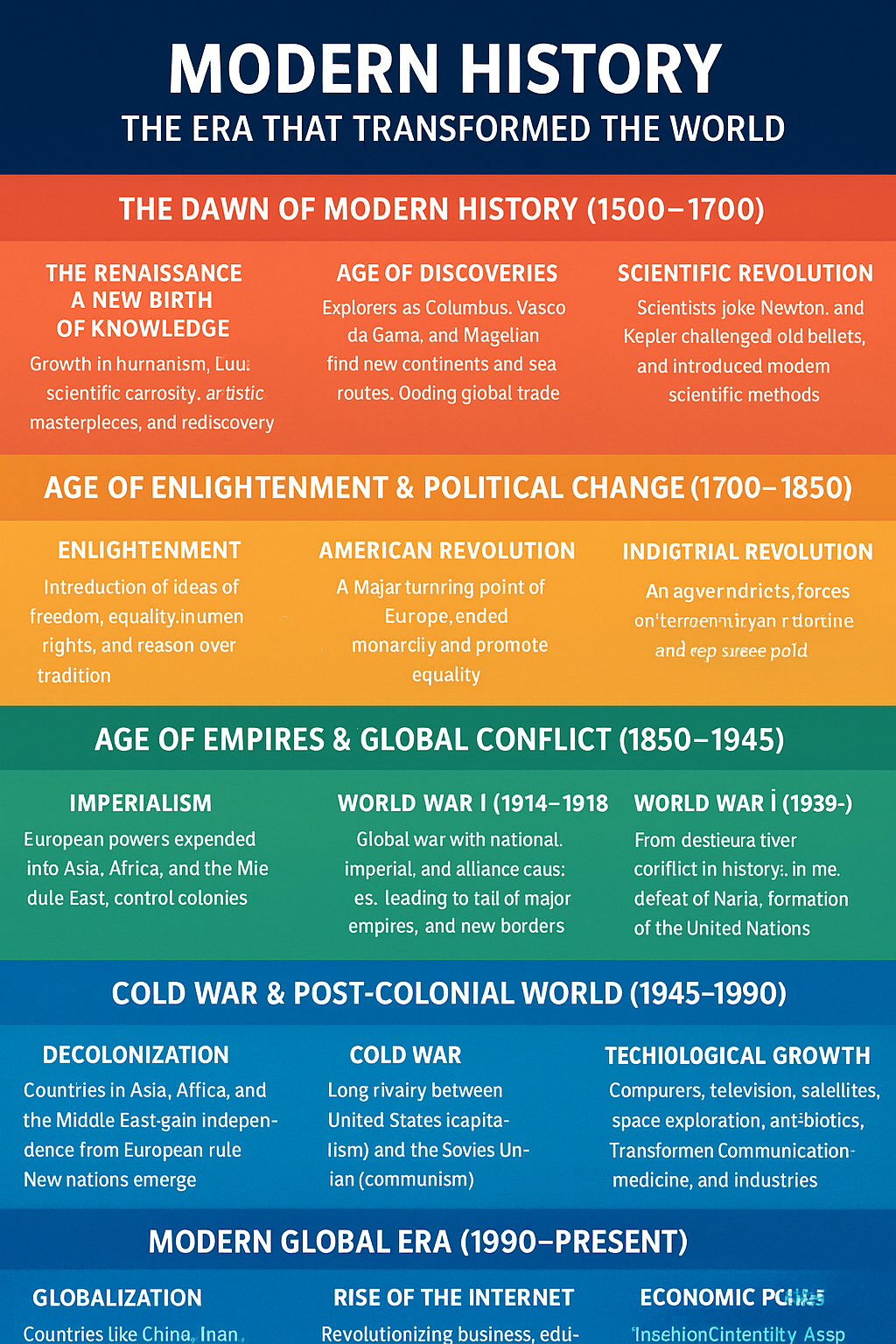
Modern History is generally defined as the time period after the Middle Ages, beginning approximately in the late 1400s. It includes:
- Age of Exploration
- Scientific Revolution
- Industrial Revolution
- Rise of Nation-States
- Colonial Expansion
- World Wars
- Cold War
- Globalization
- Digital Revolution
Each phase contributed to building today’s political systems, global trade, technology, and social structures.
1. The Age of Exploration (15th–17th Century)
The first major turning point in Modern History is the Age of Exploration, when European explorers traveled to Asia, Africa, and the Americas in search of new routes and resources. This period is important because:
- It connected the world for the first time.
- It led to the discovery of new continents.
- It began large-scale global trade.
- It boosted the rise of European powers.
Explorers like Christopher Columbus, Vasco da Gama, and Ferdinand Magellan opened sea routes that reshaped global geography and commerce.
Effects of the Age of Exploration
- Exchange of goods such as spices, gold, sugar, and cotton.
- Spread of languages and religions.
- Rise of colonial empires.
- Beginning of the global economy.
This era laid the foundation for global interactions that define the modern world.
2. Scientific Revolution and Enlightenment (16th–18th Century)
Another major development in Modern History was the rapid growth of scientific knowledge. Thinkers such as:
- Galileo Galilei
- Isaac Newton
- Johannes Kepler
changed how humans understood nature, physics, and the universe.
Key Achievements
- Discovery of gravity
- Advancement in mathematics
- Invention of the telescope and microscope
- New scientific methods
The Enlightenment followed, emphasizing human rights, democracy, and rational thinking. These ideas directly influenced modern governments and inspired revolutions around the world.
3. The Industrial Revolution (18th–19th Century)
The Industrial Revolution is one of the most searched and important periods in Modern History. It began in Britain and later spread to Europe, the United States, and eventually the world.
Major Changes
- Machines replaced manual labor
- Factories increased mass production
- Railways and steamships boosted transportation
- Urbanization increased as people moved to cities
- Birth of modern capitalism and global markets
This period not only grew global wealth but also created the modern workforce, changed family structures, and improved communication.
4. Rise of Nation-States and Modern Political Systems
During the 18th and 19th centuries, countries began forming strong central governments known as nation-states. Examples include:
- Germany
- Italy
- United States
- Japan
This era saw:
- Birth of modern constitutions
- Spread of democratic and parliamentary systems
- Growth of nationalism
- Expansion of education systems
These changes shaped the political structures we use today.
5. First World War (1914–1918)
World War I was a turning point that reshaped borders, economies, and political systems. It is one of the most widely studied events in Modern History.
Causes
- Nationalism
- Alliances
- Militarization
- Colonial rivalries
Effects
- Collapse of empires (Ottoman, Austro-Hungarian)
- Economic depression
- Rise of new political ideologies like communism and fascism
- Creation of the League of Nations
The war marked the beginning of large-scale industrial warfare.
6. Second World War (1939–1945)
World War II was the largest conflict in human history. It involved major global powers and changed international politics permanently.
Major Themes
- Rise of Adolf Hitler and Nazi Germany
- Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
- Holocaust
- Global alliances and military strategies
Impact
- Creation of the United Nations
- Start of the Cold War
- End of colonial empires
- Beginning of the modern human rights movement
WWII also accelerated technological innovation in medicine, aviation, and communication.
7. The Cold War (1947–1991)
After World War II, global power was divided between:
- United States and Western democracies
- Soviet Union and communist states
This period saw:
- Nuclear arms race
- Space race
- Creation of NATO and Warsaw Pact
- Korean and Vietnam Wars
- Political tensions without direct war
The fall of the Soviet Union in 1991 ended the Cold War and opened the path to global capitalism and free markets.
8. Decolonization and Rise of New Nations
Between the 1940s and 1970s, dozens of countries in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East gained independence from European rule. This movement:
- Redefined international politics
- Created new nations such as India, Pakistan, Nigeria, Kenya
- Spread democratic values
- Gave voice to cultural identity and human rights
Decolonization reshaped global diplomacy and the world map.
9. Age of Globalization (late 20th century–present)
Globalization is one of the most frequently searched topics in Modern History. It refers to the increased connection between countries through:
- Trade
- Technology
- Travel
- Culture
- Media
- Online communication
Key Features
- International supply chains
- Growth of multinational corporations
- Migration and cultural exchange
- Free-trade agreements
- Expansion of the internet
Globalization made the world more interconnected than ever before.
10. The Digital Revolution and 21st-Century Technology
The modern era is shaped by rapid technological growth. Innovations like:
- Smartphones
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social media
- Cloud computing
- Blockchain
- Robotics
- Renewable energy
have completely transformed communication, work, and global economies.
This period is often called the Information Age.
Impact of Modern History on Today’s World
Modern History influences every part of life today:
1. Political Impact
- Rise of democracy
- Global organizations (UN, NATO, EU)
- Human rights laws
2. Economic Impact
- Global trade
- Industrial and digital economies
- Capitalism and modern banking
3. Social Impact
- Education systems
- Women’s rights
- Urban lifestyles
4. Technological Impact
- Internet
- Transportation
- Medical advancements
Modern History explains why the world is structured the way it is today.
Conclusion
Modern History is a story of transformation, innovation, conflict, and progress. From the 15th century to the digital age, this era has shaped every part of human society — politics, economies, technologies, and cultures. Understanding Modern History helps us understand globalization, development, and the challenges the world faces today. It shows how past discoveries, revolutions, and struggles built the modern world and continue to influence our future.